Wouldn’t it be great if your business could show web ads to hot leads at any time? What if you could expand your reach to soon-to-be-buyers who have never even heard of your company?
Well, now you can achieve these objectives, with the in-market audiences feature from Google Ads. This is a welcome addition to the search advertising platform that takes targeting to the next level.
What are in-market audiences? And how can you optimize your campaigns to reach hot leads ready to buy?
Keep reading to learn all about Google Ads in-market audiences. We’ll explain how to use this feature and why it’s important for your business.
What Are Google Ads In-Market Audiences?
In-market audiences are the search giant’s powerful tool for targeting users who are heavily researching or are in-market for a particular product.
Google has offered the option since 2014, but the platform was only available across the Google Display Network publisher and partner sites and YouTube. That changed in 2018 when Google expanded the tool for search campaigns.
So how does Google know who is researching or in the buying process for a specific product or service? They utilize machine learning to analyze trillions of search queries and user website behavior. The machine examines the data to calculate the purchase intent of its users.

In-market audiences improve the ability of Google Ads to compete with other audience-based advertising options. Advertisers want more than just keyword-based search campaigns, which is why Facebook Ads deep targeting options make that platform so popular.
In-market audiences should not be confused with remarketing lists for search ads (RLSA), which allows you to retarget previous visitors to your site and entice them to return. Like RLSA, the audience you target is usually closer to a purchase than leads you find on standard search. But in-market audiences are different because it’s quite possible they have never heard of your company or visited your site before.
Now you can attract new leads who are ready to buy with in-market audiences, and then retarget them if necessary with RSLA. In this way, the two features complement each other perfectly.
Reaching new leads who are in the buying process is what makes in-market audiences so enticing to marketers. It’s the perfect compliment to retargeting.
How Does In-Market Audiences Work?
Here’s an example of how in-market audiences zero in on prospects who are close to purchasing a product.
Let’s say you run ad campaigns for a rental car service in Los Angeles. Currently, you run a campaign on the keyword phrase “rental cars in Los Angeles.”
You may attract some warm leads, but you’ll also attract people who are in the early stages of planning a vacation, which could be months away. At this point, they are seeking information, and aren’t anywhere near making a purchase.
But some of these prospects are closer to booking a rental car. They have already booked their flight and hotel and now all they need is a vehicle.
You couldn’t accurately target this sub-group of prospects using a keyword-based campaign. But you can with in-market audiences because it takes into account much more than a singular search query. The feature looks at a user’s recent search history and behavior.
In this case, in-market audiences might look at a user’s previous searches such as “flights to Los Angeles,” “Los Angeles hotels,” “attractions in Los Angeles,” and “best rental car companies in Los Angeles.”
So while you can still run Google Ad campaigns that target a specific keyword phrase, you can’t target someone’s search history with keywords. That is what makes in-market audiences unique. That’s how it gives you company a distinct advantage over other competitors who aren’t using this advertising option.
With in-market audiences, you can place higher bids, or use a larger portion of your ad spend on prospects who are ready to buy now.
How to Set Up an In-Market Audience Campaign for Search?
Setting up an in-market audience campaign in Google Ads is pretty straight-forward.
First, log-in to Google Ads and create a new ad campaign, or go to an existing one. Next, click on “Audience” in the left side-bar of your screen. You will see a blue edit icon near the top left which you need to select.
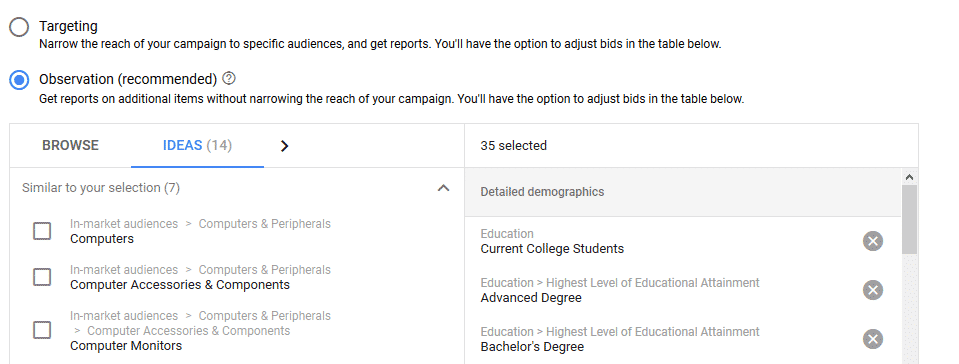
Now, click on the link that says “Select an ad group.” At this point, you’ll need to look at the list and choose your campaign and ad group. Now, select “Observation” or “Targeting” mode; We recommend choosing “Observation” to start.
Select the area that says “‘What they’re actively researching or planning.’ A list of in-market audience categories will now appear. Select the most appropriate one for your ad campaign. Many of these categories will have subcategories that you can add to your campaign where it is appropriate to your business.
Best Practices for Using In-Market Audiences
If you’re new to in-marketing audiences, we recommend starting slowly as you learn the ropes. Add an audience to one of your existing campaigns and begin with a low bid to test the waters.
Here are a few tips to guide you along the way.
1. Test, Test, Test
In-market audiences campaigns are like any other type of advertising. In order to optimize your campaigns to the fullest, you must continuously test your ads. Through testing, you can simultaneously lower your bid costs and improve your ROI.
A/B testing is the most common and effective way to test any variable in your campaign. Take your ad copy, for instance. It is wise to set up a control campaign (A) and another separate campaign (B) to test different variations.
With your B campaign, test one variable at a time. For example, you might try different headlines one week. When you find a headline that improves your click-through rate (CTR), add that headline to your control campaign.
Your “A” campaign is your primary campaign. Only make changes to it when your “B” testing demonstrates better performance of a particular variable. In this way, your primary campaign is always improving.
2. Use Observation Mode
Google Ads gives you the option to use either target or observation modes. Most of the time you will want to select observation mode, which allows you to analyze how an audience performs. Over the course of a week or two, you can discover valuable data that will illuminate what your next move should be.
For example, when you see a particular audience is both large and responsive, you should create a separate campaign under the targeting option.
Targeting mode, on the other hand, does not reach as many web users. However, the prospects it finds are in the “buy now” phase and convert at a higher rate. Only use this option if you only want to target only those who are close to the point of purchase.
3. Layer In Additional Markets
You can really hyper-target prospects by layering in-market audiences with a similar audience. Not to mention you can add other demographics, such as age and gender.
This is how you expand your prospect reach to find new customers your competitors are overlooking.
4. Test Multiple Audiences
Every industry has it’s shoulder niches that are closely related but not exactly the same. By testing multiple audiences, you can extend your reach without necessarily facing more competition within your industry.
Let’s say your company sells athletic shoes. You can observe an audience strictly containing people looking for shoes. But you can also add in other audiences who will also need shoes, such as people who are currently buying running clothes. The same goes for audiences interested in basketball, CrossFit, hiking and a host of other activities.
5. Combine In-Market Audiences with Remarketing
If you really want to boost sales, use in-market audiences together with retargeting. Take advantage of this in Google Ads to reach leads who are already interested in your brand and they want to buy what you’re selling.
This is an effective strategy to catapult your conversion rates and ROI.
6. Do What Already Works
If you are already using Google Ads, you likely know how to create campaigns and choose keywords that target prospects who have the intent to buy. For instance, if you sell surfboards, you are might be using keywords such as “surfboards on sale,” “cheap surfboards,” or “buy a surfboard.”
If one or more of these campaigns are proven winners for you, then why not use the same headline and ad copy to target in-market audiences? It’s a great place to start and you can tweak your ads as necessary.
Even if your company does not yet use Google Ads, you can still look at the ad results for similar buying keywords that relate to your industry. Do you notice a particular sponsored ad that is consistently at the top of the results on Google? If so, chances are it’s a successful ad that is working for the advertiser.
You can create a similar ad and test changes as you go to improve the CTR.
Doing what already works is one way to avoid making the most common mistakes committed by advertisers.
7. Closely Monitor Your Campaigns
The only way you will know if an ad is working is by monitoring a campaign’s performance. Thankfully, the Google Ads platform delivers a wealth of metrics and information so you can determine if your marketing efforts are profitable.
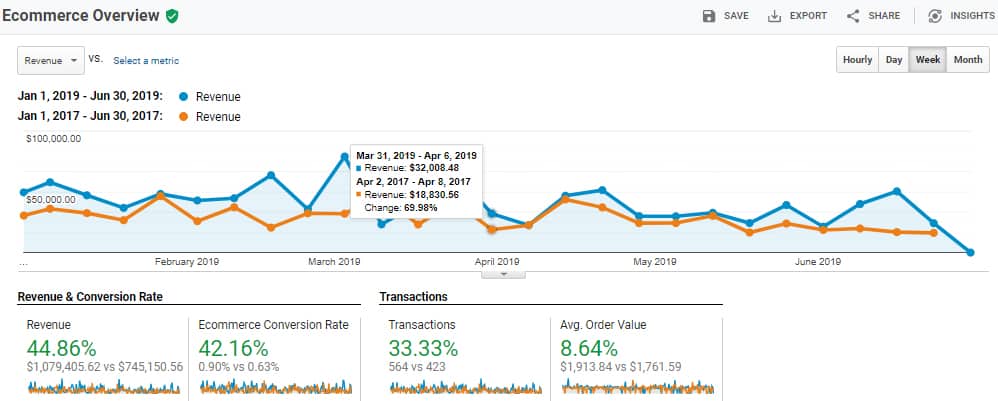
An obvious way to tell if your ads are working is to compare your company’s sales growth numbers against your ad spend. Do you have a profit margin or are you operating at a loss?
If your ad is breaking even, that’s actually a good sign. With some testing, you can improve your ad copy and optimize your campaign to make the campaign profitable.
If you’re not making many sales, turn to Google’s analytics to figure out why. Start with your CTR. If it’s low, then you need to improve your ad headline and text. If the CTR is high, that means your landing page is not converting to sales.
Another important metric is your campaign’s Quality Score. Google will limit your ad’s exposure if the score is low. In that case, take the necessary steps to improve your score so you can reach a larger audience.
For more tips to optimize your campaigns, check out these Google ad hacks that drive more leads.
What Markets Are Available?
Google offers nearly 200 unique in-market audiences spread out over 19 main categories.
The main categories you can target are as follow:
- Baby & Children’s Products
- Beauty Products & Services
- Business Services
- Cars & Vehicles
- Clothing & Accessories
- Computers & Peripherals
- Consumer Electronics
- Dating Services
- Education
- Employment
- Event Tickets
- Financial Services
- Gifts & Occasions
- Home & Garden
- Property
- Software
- Sports & Fitness
- Telecom
- Travel
As you’ll see, each category contains its own subcategories. And many categories have their own categories as well. The more you can drill down and hyper-target your prospects, the better your CTR and ROI will be.
Simply choosing one top-level category may work to some extent, but you’ll also waste money on clicks from tire-kickers who aren’t ready to buy yet. Use subcategories to your advantage to hone in on your best prospects.
Final Thoughts
So the final question is, “Do in-market audiences really work?” The answer is a resounding “yes” with the caveat that you must use them correctly.
For example, before you spend a dollar on advertising, you must test your landing page and prove it can convert. The copywriting on this page needs to be persuasive and include a sales offer that is irresistible.
Your buying process has to be simple and effortlessly guide prospects to the point of purchase.
With your landing page ready for sales, it’s time to create an ad campaign. Start by using keyword campaigns that already work for you and make a similar campaign for in-market audiences.
It may take time to become proficient advertising to in-market audiences but the process is well worth it. Of course, if you would rather leave the duties to a professional agency, we would love to help. Contact us now to schedule a confidential consultation.